Face Recognition
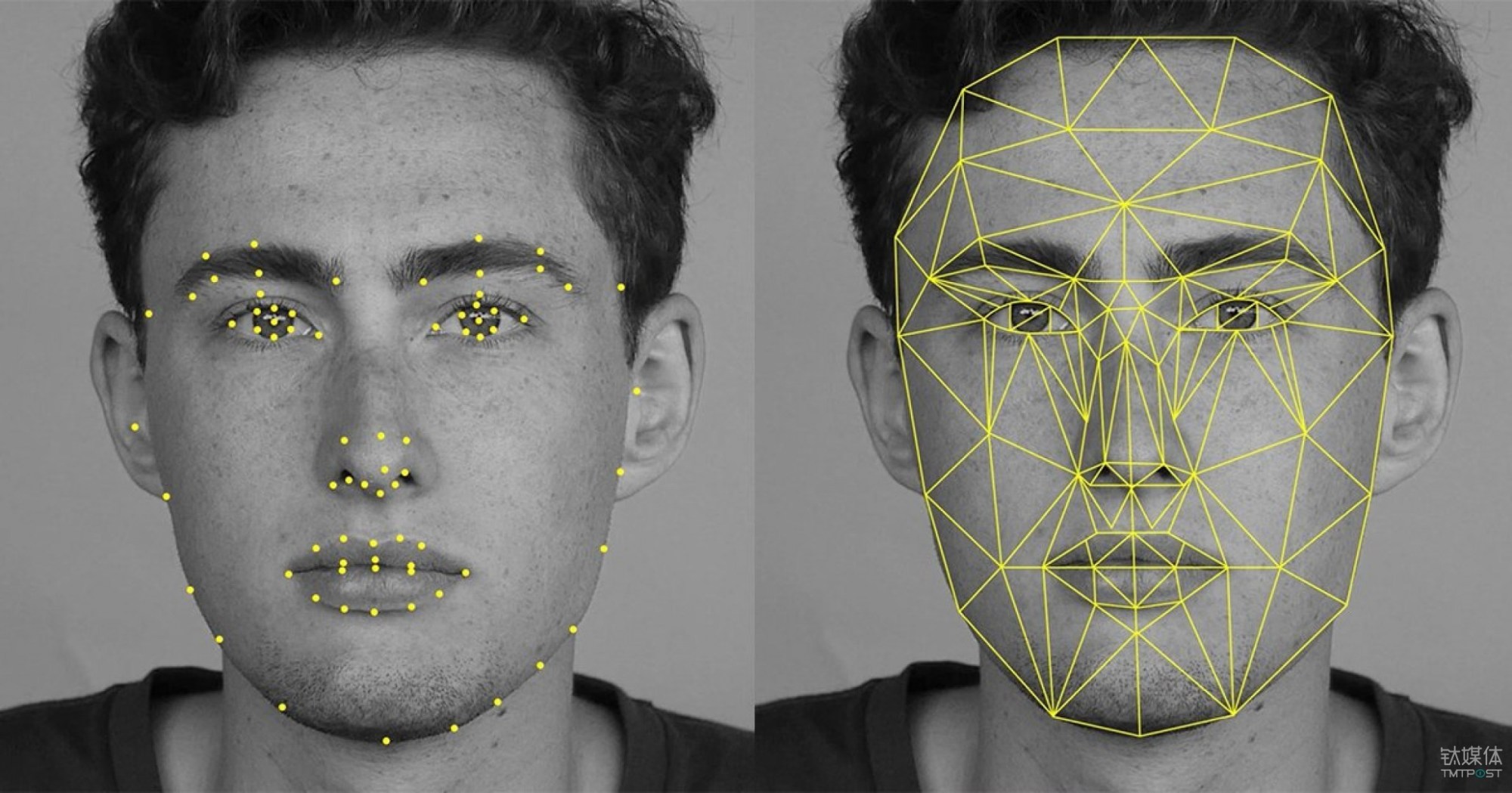
Verification vs. recognition
- Facial recognition is a biometric solution that measures unique characteristics about one’s face.
- Face verification is concerned with validating a claimed identity based on the image of a face, and either accepting or rejecting the identity claim (one-to-one matching)
- The goal of face identification is to identify a person based on the image of a face (one-to-many matching)
Difficulties
- We cannot use plain classification for face recognition for two reasons:
- CNN doesn’t work on a small training sets, since a vanilla cross-entropy-loss softmax classifier severely overfits to the limited data,
- It is not convenient to retrain the model every time we add a picture of a new person to the system.
- Also, we cannot use similarity functions like L2 distance, which suffer from the ominous sounding curse of dimensionality and so won’t work well for data with thousands of dimensions.
- But we can use a deep convolutional network to learn some kind of similarity function that a classifer like nearest neighbor can use to classify a face.
One-shot learning
- One-shot learning is an object categorization problem in computer vision, which aims to learn information about object categories from one, or only a few, training images.
Siamese network
- Siamese NNs are popular among tasks that involve finding similarity or a relationship between two comparable things.
- Instead of a model learning to classify its inputs, the neural networks learn to differentiate between two inputs. They learn the similarity between them.
- Siamese networks are best-suited for cases where we can have only a few examples per class.
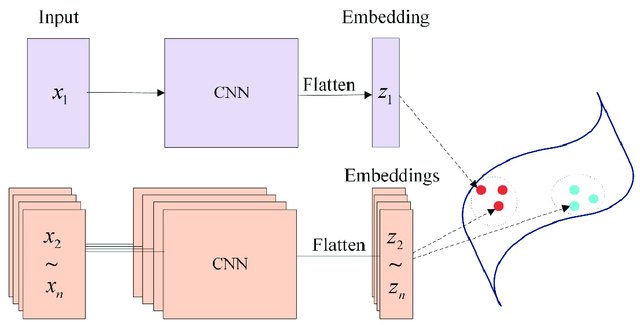
- Siamese neural network is a class of neural network architectures that contain two or more identical subnetworks (identical here means they have the same configuration with the same parameters and weights)
- Parameter updating is mirrored across both subnetworks.
- The last layers of the two networks are fed to a loss function, which calculates the similarity between the embeddings.
- You can also learn the similarity function by letting the network adjust the weights and biases of the logistic regression.
- Siamese Neural Networks for One-shot Image Recognition (2015)
- One Shot Learning and Siamese Networks in Keras
Embeddings
- Embedding is projecting input features to a some higher-dimensional space.
- It means converting data to a feature representation where certain properties can be represented by notions of distance (such as semantic similarity)
- In the embedding space, similar features should be close together and form well-separated clusters.
- Furthermore, an SVM classifier or any other simple multi-class classifier can be trained to cluster vector embeddings effectively.
- For further details, see Word Embeddings

Pros
- Sharing weights across subnetworks means fewer parameters to train for.
- Robustness to class imbalance:
- If the model has learnt well what makes any classes the same, one example of an another class in training may be sufficient to predict this class in the future.
- Ensembling with best classifier:
- Given that its learning mechanism is somewhat different from classification, simple averaging of it with a classifier can do much better than averaging two correlated supervised models.
- Better embeddings:
- Siamese focus on learning embeddings (in deeper layer) that place same classes close together. Hence, it can learn semantic similarity.
Cons
- Training involves pairwise learning and thus slower than classification (pointwise learning)
- Prediction can be slightly slower:
- It does not readily output class probabilities, but distances from each class.
Similarity functions
Contrastive loss
- Contrastive loss is a distance-based loss function (as opposed to prediction error-based loss functions)
- Takes a pair of images and trains the embeddings so that the distance between them is minimized if they're from the same class and is greater than some margin value if they represent different classes.
$$\large{L(X_1,X_2)=(1-Y)\frac{1}{2}d(X_1,X_2)^2+Y\frac{1}{2}{\max{(0,m-d(X_1,X_2))}}^2}$$
- Intuitively, this function just evaluates how well the network is distinguishing a given pair of images.
- Margin \(m\) is used to determine the limit to which examples from different pairs are penalized.
- How to set the margin:
- Margin depends on the number of features and their magnitude so it's hard to set it as a constant.
- The margin should be set automatically while training.
- Or just normalize features using L2 before using contrastive loss and use a constant.
- Dimensionality Reduction by Learning an Invariant Mapping (2005)
Triplet loss
- Triplet loss is one of the loss functions we can use to solve the similarity distance in a Siamese network.
- The goal of the triplet loss is to make sure that two examples with the same label have their embeddings close together in the embedding space, while two examples with different labels have their embeddings far away.
- Each training sample is actually composed of a "triplet" of examples: anchor \(A\), a positive of the same class as the anchor \(P\), and a negative of a different class \(N\).
- The contrastive loss, on the other hand, only considers pairwise examples at a time.
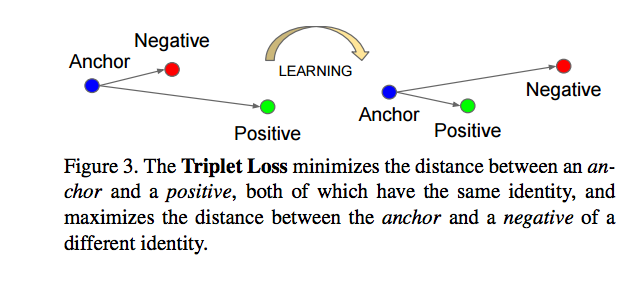
- Implementation:
- Encode triplets as embeddings in some vector space.
- Calculate the two distances \(d(A,P)\) and \(d(A,N)\) in the embedding space.
- Define a margin so that minimizing the loss both pushes \(d(A,P)\) to zero, and \(d(A,N)\) to be bigger than \(d(A,P)+m\). This is very similar to the margin used in SVMs. Having a margin indicates that dissimilar pairs that are beyond this margin will not contribute to the loss.
$$\large{L(A,P,N)=\frac{1}{n}\left(\sum_{i=1}^{n}{\max{(d(A_i,P_i)-d(A_i,N_i)+m,0)}}\right)}$$
- Requires training with multiple images of the same face.
- If we choose them randomly, it will be too easy to satisfy the constraint of the loss function because the distance is going to be most of the time so large.
- We need to find \(A\), \(P\), and \(N\) so that \(A\) and \(P\) are close to \(N\).
- Our objective is to make it harder to train the model to push the gradient descent to learn more.
- Triplet Loss and Online Triplet Mining in TensorFlow
- Siamese and triplet learning with online pair/triplet mining
Binary classification
- Binary classification is another way to learn the similarity function, e.g., using Manhattan distance and sigmoid layer
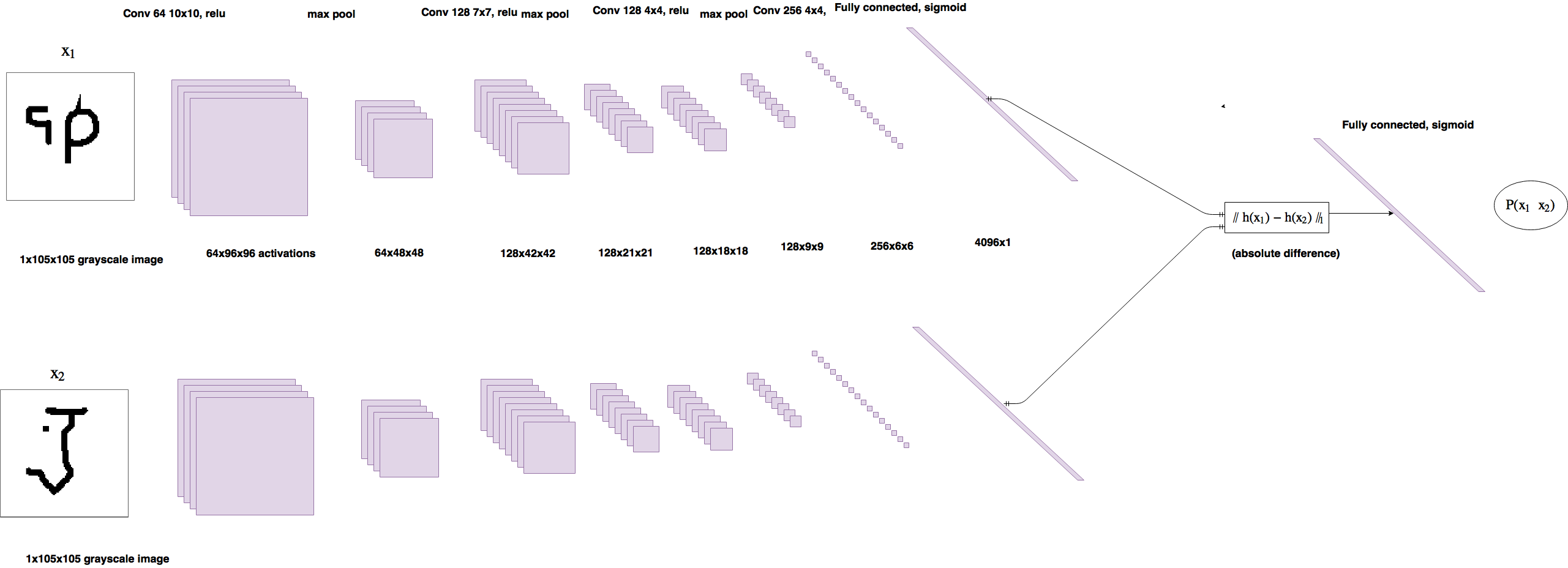
FaceNet
- FaceNet is the backbone of many open source face recognition system like OpenFace
- FaceNet uses Siamese network to transform a face into 128D Euclidian space similar to word embedding
- DeepFace: Closing the Gap to Human-Level Performance in Face Verification (2014)
- FaceNet: A Unified Embedding for Face Recognition and Clustering (2015)
- Deep Face Recognition (2015)