Applications
Decoupling services
- Decoupled architecture is a type of computing architecture that enables computing components or layers to execute independently while still interfacing with each other.
SQS
- Amazon Simple Queue Service (SQS) is a fully managed message queuing service that enables you to decouple and scale microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications.
- Using SQS, you can decouple the components so that they run independently.
- Resolves issues if producer produces work faster or both components only loosely connected.
- A queue is a temporary repository for messages that are awaiting processing.
- The queue acts as a buffer between the producing and receiving components.
- Any component of a distributed application can store messages in a fail-save queue.
- The queue redundantly stores the messages across multiple Amazon SQS servers.
- In IT the term 'message' can be used in the common sense, or to describe a piece of data of Task in an asynchronous queueing system such as MQseries, RabbitMQ or SQS.
- Messages can contain up to 256KB of text in any format (or 2GB with S3)
- Messages can be retrieved using the AWS SQS API.
- SQS is pull based, not push based.
- You can set the message retention period to a value from 60 seconds to 14 days.
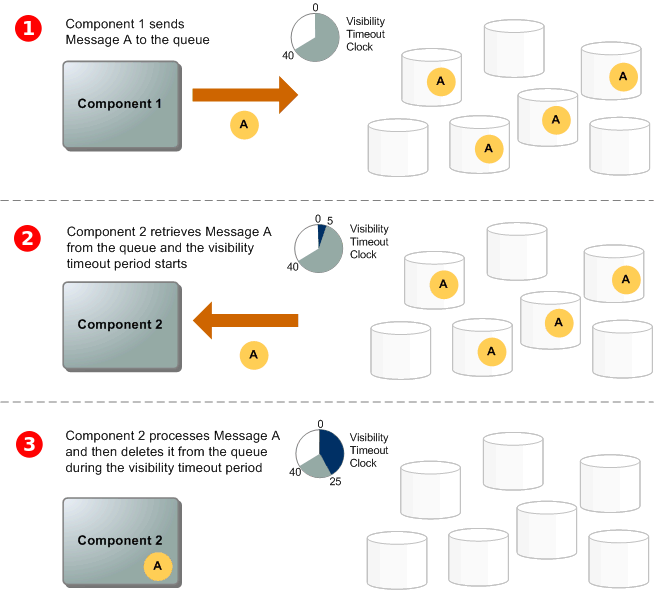
- Visibility timeout:
- The visibility timeout controls how long a message is invisible in the queue while it is being worked on by a processing instance.
- If the message is processed before the timeout, it becomes deleted. Otherwise, it becomes visible again. This can result in the same message being delivered twice.
- This interval should not be confused with how long the message can remain in the queue.
- Visibility timeout maximum is 12 hours.
- Long polling:
- Won't return a response until a message arrives in the message queue, or it times out.
- Enable long polling by setting
ReceiveMessageWaitTimeSeconds > 0 - Helps reduce the cost of using SQS by eliminating the number of empty and false responses.
- Messages being sent twice in an SQS queue configured with long polling is quite unlikely.
- Poor timing of SQS processes can significantly impact the cost effectiveness of the solution:
DelaySeconds: When a new message is added to the SQS queue, it will be hidden from the consumer instances for a fixed period.VisibilityTimeout: When a consumer instances receives a message, that message will be hidden from other consumer instances for a fixed period.WaitTimeSeconds: When the consumer instance polls for new work, the SQS service will allow it to wait a certain time for one or more messages to be available before closing the connection.
- Priority queues:
- It is best to create separate SQS queues for each priority.
- The SQS queues for with the highest priority will be polled first by consumers.
- What Is Amazon Simple Queue Service?
- Basic Amazon SQS Architecture
- Amazon SQS Cheat Sheet
Types
- Standard queues:
- Nearly an unlimited number of transactions per second, at-least-once processing, and the order is not preserved.
- SQS uses multiple hosts, and each host holds only portion of all the messages. When a consumer calls for a new message, it does not see all the hosts or all the messages. As such, messages are not necessarily delivered in the order in which they were generated.
- If an agent abandons a message or takes a break before finishing a message, it will be offered in the queue again. In order to ensure that no message is lost, a message will persist in the SQS queue until it is processed successfully.
- FIFO queues:
- FIFO delivery, exactly-once processing, and the order is preserved.
MQ
![]()
- Amazon MQ supports industry-standard APIs and protocols so you can switch from any standards-based message broker to Amazon MQ without rewriting the messaging code in your applications.
- Using Amazon SQS requires you to do additional changes in the code.
- But if you are building brand new applications in the cloud, then it is highly recommended that you consider Amazon SQS and Amazon SNS.
- Amazon MQ FAQs
- How Is Amazon SQS Different from Amazon MQ or Amazon SNS?
- Amazon MQ Cheat Sheet
SWF
- Amazon Simple Workflow Service (Amazon SWF) makes it easy to build applications that coordinate work across distributed components.
- Used by Amazon.com for orders, payments, warehousing, etc.
- Tasks represent invocations of various processing steps.
- For example, executable code, web service calls, human actions, and scripts.
- Concepts:
- Actors: An application that can initiate a workflow.
- Deciders: Control the flow of activity tasks in a workflow execution.
- Activity workers: Carry out activity tasks.
- Domains: Collections of related workflows.
- By default, each workflow execution can run for a maximum of 1 year in Amazon SWF.
- While there are a limited range of SDKs available for SWF, AWS provides an HTTP based API which allows you to interact using any language as long as you phrase the interactions in HTTP requests.
- Amazon SWF Cheat Sheet
Compared to SQS
- Similar to SQS, SWF manages queues of work, however unlike SQS it can have out-of-band parallel and sequential task to be completed by humans and non AWS services.
- With SWF, workflow executions can last up to 1 year.
- SQS has retention period of up to 14 days.
- SWF presents a task-oriented API.
- SQS presents a message-oriented API.
- SWF ensures that a task is assigned only once and is never duplicated.
- With SQS you may handle duplicated messages and need to ensure that a message is processed only once (FIFO)
- SWF keeps track of all tasks and events in an application.
- In SQS you need to implement your own application-level tracking, especially if your applications uses multiple queues.
SNS
- Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) is a highly available, durable, secure, fully managed pub/sub messaging service that enables you to decouple microservices, distributed systems, and serverless applications.
- Makes it easy to set up, operate, and send notifications from the cloud.
- Provides developers with a highly scalable, flexible, and cost-effective capability to publish messages from an application and immediately deliver them to subscribers or other applications.
- Besides pushing cloud notifications directly to mobile devices, Amazon SNS can also deliver notifications by SMS, email, or any HTTP endpoint.
- Allows grouping multiple recipients using topics.
- For example, using topics, you can group together iOS, Android, and SMS recipients.
- When you create a topic on Amazon SNS, an ARN is created.
- To prevent messages from being lost, all messages are stored redundantly across multiple AZs.
- Benefits:
- Instantaneous, push-based delivery (no polling)
- Simple APIs and easy integration with applications.
- Flexible message delivery over multiple transport protocols.
- Inexpensive, pay-as-you-go model with no up-front costs.
- AWS Management Console offers the simplicity of a point-and-click interface.
Compared to SQS
- Both are messaging systems in AWS.
- SQS is pull-based, whereas SNS is push-based.
Elastic Transcoder
- Media transcoder in the cloud.
- Converts media files into different formats that will play on smartphones, tables, PCs, etc.
- Provides transcoding presets for popular output formats.
- Pay based on the minutes that you transcode and the resolution at which you transcode.
API Gateway
- Amazon API Gateway is a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale.
- You can create an API that acts as a "front door" for applications to access data, business logic, or functionality from your back-end services, such as applications running on EC2 instances, code running on Lambda, or any web application.
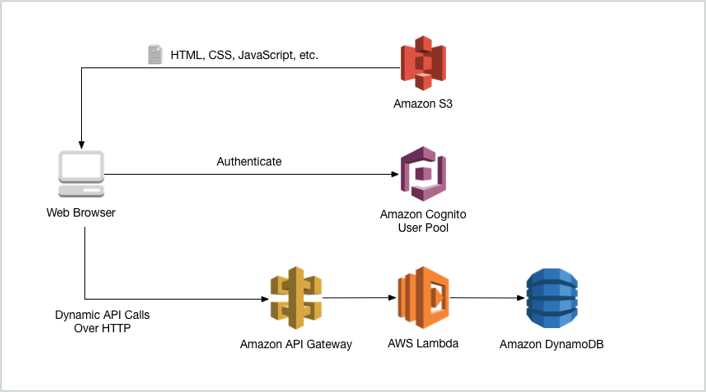
- Features:
- Expose HTTP endpoints to define a RESTful API.
- Serverlessly connect to services like Lambda and DynamoDB.
- Send each API endpoint to a different target.
- Track and control usage by API keys.
- Throttle requests to prevent attacks.
- Connect to CloudWatch to log all requests for monitoring.
- Maintain multiple versions of your API.
- API Gateway is low cost and scales automatically.
- How to configure API Gateway:
- Define an API (container)
- Define resources and nested resources (URL paths)
- For each resource, select supported HTTP methods, set security, choose the target (e.g. Lambda), and set request and response transformations.
- How to deploy API Gateway:
- Deploy API to a stage: Uses the API Gateway domain by default, but you can use a custom domain.
- Now supports AWS Certificate Manager: free SSL/TLS certificates.
- Request throttling:
- Throttling limits can be set for standard rates and bursts (for a few seconds)
- Any request over the limit will receive a 429 HTTP response.
- Throttling and Caching
- You can enable API caching to cache your endpoint's responses.
- With caching, you can reduce the number of calls and improve performance.
- API Gateway caches responses for a specific TTL period, in seconds.
- Same Origin Policy:
- Under the policy, the web browser permits scripts contained in a first web page to access data in a second web page, but only if both web pages have the same origin (domain name)
- This is done to prevent Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks.
- Enforced by web browsers, but ignored by tools such as Postman and curl.
- If you're using JS/AJAX that uses multiple domains with API Gateway, ensure that you have enabled CORS on API Gateway.
- Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) is a mechanism that allows restricted resources (e.g. fonts) on a web page to be requested from another domain outside the domain from which the first resource was served.
- The way that server at the other end (not the client side) can relax SOP.
- CORS is enforced by the client.
- Billing:
- You pay only for the API calls you receive and the amount of data transferred out.
- You can use AWS X-Ray to trace and analyze user requests as they travel through your Amazon API Gateway APIs to the underlying services.
- X-Ray gives you an end-to-end view of an entire request, so you can analyze latencies in your APIs and their backend services.
- Amazon API Gateway FAQs
- Amazon API Gateway Cheat Sheet
Kinesis
- Streaming data is data that is generated continuously by many data sources, which typically send in the data records simultaneously, and in small sizes (order of KB)
- For example, purchases of an online store, stock prices and game data.
- Amazon Kinesis is a platform on AWS to send your streaming data to.
- Kinesis makes it easy to load and analyze streaming data, and build custom applications.
Types
- Kinesis Data Streams:
- A massively scalable and durable real-time data streaming service.
- KDS can continuously capture gigabytes of data per second from hundreds of thousands of sources such as website clickstreams, database event streams, financial transactions, social media feeds, IT logs, and location-tracking events.
- Data is stored in shards that are then processed by consumers (EC2 instances)
- Per shard, allows 5 transactions per second for reads, up to a maximum total data read rate of 2 MB per second and up to 1000 records per second for writes, up to a maximum total data write rate of 1 MB per second (including partition keys)
- Persistently stores streaming data for 24 hours and up to 7 days.
- The data capacity of your stream is the sum of the capacities of its shards.
- A Kinesis data stream stores records from 24 hours by default to a maximum of 168 hours.
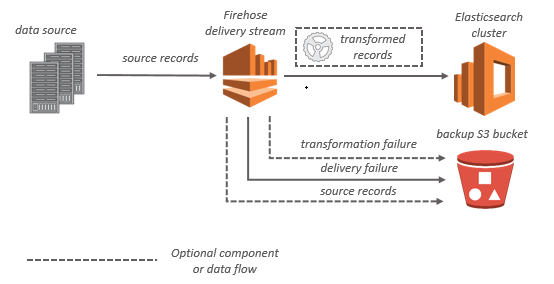
- Kinesis Data Firehose:
- The easiest way to reliably load streaming data into data lakes, data stores and analytics tools.
- A fully managed service that automatically scales to match the throughput.
- Can capture, transform, and load streaming data into S3, Redshift, Elasticsearch, and Splunk.
- Can also batch, compress, transform, and encrypt the data before loading it.
- Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose
- Kinesis Data Analytics:
- Enables you to build queries and sophisticated streaming applications with SQL or Java.
- Can use Data Streams or Data Firehose as an underlying streaming service.
- Kinesis Video Streams:
- Makes it easy to securely stream video from connected devices to AWS.
- Amazon Kinesis Cheat Sheet


