Databases
- Stateless applications:
- The essence of a stateless installation is that the scalable components are disposable, and configuration is stored away from the disposable components.
- Elasticache is well suited for very short fast cycle data.
- RDS is well suited for structured and long cycle data.
- DynamoDB is well suited for unstructured and medium cycle data.
RDS
- Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) makes it easy to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the cloud.
- Can be optimized for memory, performance or I/O
- Use IOPS for OLTP in production environment.
- To increase the number of IOPS available to a MySQL database on the root volume of an EC2 instance, add (at minimum) 4 additional EBS SSD volumes and create a RAID 10 using these volumes.
- RDS supports the MariaDB, PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLServer, Oracle, and Aurora database engines.
- Microsoft SQL Server database engine can have the maximum size of 16TB.
- MySQL installations default to port number 3306.
- The RDS instance port number is automatically applied to the RDS DB Security Group.
- RDS runs on virtual machines.
- You cannot RDP or SSH into an RDS instance however.
- Patching of the RDS operating system and DB is Amazon's responsibility.
- RDS is not server-less (with exception of Aurora)
- Encryption:
- Encryption at rest is done using the AWS KMS service.
- RDS's storage, automated backups, read replicas, and snapshots are encrypted as well.
- You can authenticate to DB instance using IAM DB authentication.
- With this authentication method, you don't need to use a password when you connect to a DB instance. Instead, you use an authentication token.
- An authentication token is a unique string of characters that Amazon RDS generates on request.
- The IAM database authentication works with MySQL and PostgreSQL.
- Security groups:
- With a DB security group the RDS instance port number is automatically applied.
- Monitoring:
- CloudWatch gathers metrics about CPU utilization from the hypervisor for a DB instance. It does not provide the percentage of the CPU bandwidth and total memory consumed by each database process in your RDS instance, since you do not have direct access to the instances/servers of your RDS database instance and so cannot install a CloudWatch agent.
- Enhanced Monitoring gathers its metrics from an agent on the instance (more preferable). It helps you identify which processes are having the greatest impact on performance: RDS child processes, RDS processes, and OS processes.
- Viewing Enhanced Monitoring by Using CloudWatch Logs
- Monitoring with Amazon CloudWatch
- Boosting performance:
- Provision a larger RDS instance with provisioned IOPS.
- Add an RDS Read Replica for increased read performance.
- Use ElastiCache to cache frequently read, static data.
- Limits:
- Oracle has a limit of 1 database on a single instance.
- SQL Server has a limit of up to 100 databases on a single instance.
- Both the Oracle and SQL Server database engines have limits due to licensing.
- The open-source database engines such as Aurora, MySQL, MariaDB or PostgreSQL have no such limits.
- Amazon RDS FAQs
- Amazon RDS Cheat Sheet
Multi-AZ
- Allows you to have an exact copy of your production database in another AZ.
- Writes to the production database are automatically synchronized to the standby database.
- The standby instance will not perform any read and write operations while the primary is running.
- Failover:
- In case of planned database maintenance, instance failure, or an AZ failure, Amazon RDS will automatically failover to the standby without any administrative intervention.
- When failing over, Amazon RDS simply flips the CNAME record to point at the standby.
- You can force a failover from one AZ to another by rebooting the RDS instance.
- Used primarily for disaster recovery (DR), not for improving performance.
- Available for all databases except Aurora (it is completely fault-tolerant by default)
- RDS Reserved instances are also available for Multi-AZ deployments.
- Amazon RDS Multi-AZ Deployments
Read replica
- Allows you to have a read-only copy of your production database.
- Provides an asynchronous replication instead of synchronous.
- There is no charge associated with data transfer.
- Used primarily for very read-heavy database workloads.
- Must have automatic backups turned on.
- Up to 5 read replicas can be created.
- Can be created from another read replicas (but watch out for latency)
- Can be created from a Multi-AZ database.
- Can be created in another region.
- Has its own DNS endpoint.
- Can be Multi-AZ.
- Can be promoted to be its own database.
Backups
- Automated backups:
- Recover the database to any point in time within a "retention period".
- The retention period can be within one and 35 days.
- Takes a full daily snapshot and also stores transaction logs throughout the day.
- Recovery: Chooses the most recent backup and then applies transaction logs.
- With new RDS DB instances, automated backups are enabled by default.
- The backup data is stored in S3 and the storage is free (= the size of DB)
- Backups are taken within a specified time window.
- Database snapshots:
- Done manually (i.e. user initiated)
- They are stored even after you delete the original RDS instance, unlike automated backups.
- One can take a final snapshot before deleting the RDB.
- The restored version of the database with be a new RDS instance with a new DNS endpoint.
original.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.comtorestored.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com
- During a database snapshot or backup, I/O may be briefly suspended while the backup process initializes (typically under a few seconds), and you may experience a brief period of elevated latency.
- In RDS, changes to the backup window take effect immediately.
Aurora (serverless)
- Amazon Aurora is a MySQL-compatible relational database management system (RDBMS) that combines the speed and availability of high-end commercial databases with the simplicity and cost-effectiveness of open source databases.
- Up to five times better performance than MySQL at a price point one tenth that of a commercial RDBMS.
- Built from scratch by Amazon.
- Amazon Aurora is a MySQL and PostgreSQL-compatible relational database.
- Starts with 10GB and auto-scales in 10GB increments to 64TB.
- Computes resources can scale up to 34vCPUs and 244GB of memory.
- Amazon Aurora typically involves a cluster of DB instances instead of a single instance.
- Maintains a total of 6 copies of data: 2 copies in each AZ with minimum of 3 AZ's.
- Thus, Aurora is available only in regions with minimum of 3 AZ's.
- Designed to transparently handle the loss of up to two copies of data without affecting write availability and up to three copies without affecting read availability.
- Aurora storage is self-healing:
- Data blocks and disks are continuously scanned for errors and repaired automatically.
- Two types of replicas available:
- Aurora replicas with automatic failover (currently 15)
- MySQL read replicas (currently 5)
- Backups:
- Automatic backups are always enabled.
- Backups do not impact database performance.
- You can take snapshots, also without impacting database performance.
- You can share Aurora snapshots with other AWS accounts.
- Endpoints:
- For certain Aurora tasks, different instances or groups of instances perform different roles.
- Using endpoints, you can map connection to the appropriate instance group based on your use case.
- The custom endpoint provides load-balanced database connections based on criteria other than the read-only or read-write capability of the DB instances.
- For example, you might direct internal users to low-capacity instances for report generation or ad hoc (one-time) querying, and direct production traffic to high-capacity instances.
- Amazon Aurora Connection Management
- A MySQL database can be migrated to Aurora by creating an Aurora replica and then promoting it, or creating a snapshot and then restoring from it.
- Amazon Aurora Cheat Sheet
DynamoDB (serverless)
- Amazon DynamoDB is a fast and flexible NoSQL database service for all applications that need consistent, single-digit millisecond latency at any scale.
- It is a fully managed database and supports both document and key-value data models.
- Use cases:
- Managing items in a document format such as JSON, XML, and HTML.
- DynamoDB Time-to-Live (TTL) mechanism enables you to manage web sessions.
- Smaller data elements (such as metadata) or file pointers are best saved in DynamoDB.
- Great fit for mobile, web, gaming, ad-tech, IoT, and many other applications.
- Highly efficient:
- The database is partitioned across a number of nodes.
- Stored on SSD storage.
- Highly durable:
- DynamoDB data is automatically replicated across three different AZs.
- DynamoDB lends itself better to supporting stateless web/app installations than RDS.
- DynamoDB allows for the storage of large text and binary objects.
- But there is a limit of 400 KB which includes both attribute name and value lengths.
- The DynamoDB low-level API accepts HTTP(S) POST requests as input.
- Accepts Headers attributes Host, Accept-Encoding, Content-Length, User-Agent, Content-Type, Authorization, X-Amz-Date, and X-Amz-Target
- Pricing:
- There will always be a charge for provisioning read and write capacity and the storage of data.
- There is no charge for the transfer of data into DynamoDB, providing you stay within a single region (if you cross regions, you will be charged at both ends of the transfer)
- There is no charge for the actual number of tables you can create in DynamoDB, providing the RCU and WCU are set to 0, however in practice you cannot set this to anything less than 1 so there always be a nominal fee associated with each table.
- Consumption:
- Consumption is measured in terms of load on each individual partition, as well as load on each Local & Global Secondary Index.
- If you receive a
ProvisionedThroughputExceededExceptionerror, the throughput is not balanced across your partitions. - Use partition keys with high-cardinality features to distribute the I/O requests evenly and not avoid "hot" partitions.
- A composite primary key will provide more partition for the table and in turn, improves the performance.
- Designing Partition Keys to Distribute Your Workload Evenly
- DynamoDB Streams:
- Whenever an application creates, updates, or deletes items in the table, DynamoDB Streams writes a stream record with the primary key attribute(s) of the items that were modified.
- Can be configured to include the "before" and "after" images of modified items.
- With triggers, you can build applications that react to data modifications in DynamoDB tables.
- Remember that the DynamoDB Stream feature is not enabled by default.
- Capturing Table Activity with DynamoDB Streams
- Tutorial: Processing New Items in a DynamoDB Table
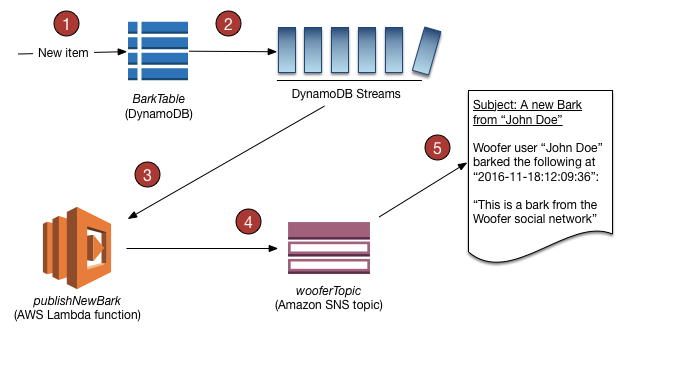
- Scales well due to these reasons:
- Its schema flexibility lets DynamoDB store complex hierarchical data within a single item.
- Composite key design lets it store related items close together on the same table.
- Amazon DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX):
- A fully managed, highly available, in-memory cache that can reduce Amazon DynamoDB response times from milliseconds to microseconds.
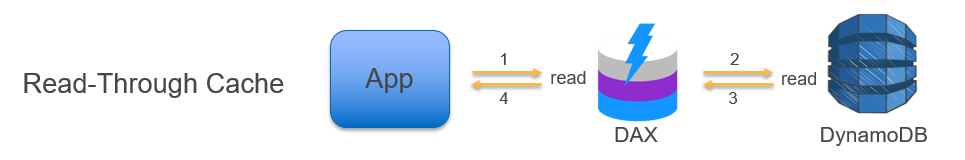
- If a shard iterator expires unexpectedly:
- The DynamoDB table used by Kinesis does not have enough capacity to store the lease data.
- Amazon DynamoDB FAQs
- Amazon DynamoDB Cheat Sheet
Modeling
- You design your schema specifically to make the most common and important queries as fast and as inexpensive as possible.
- You don’t think servers:
- The biggest entity that concerns you is a table. And anything beyond that is a dark box.
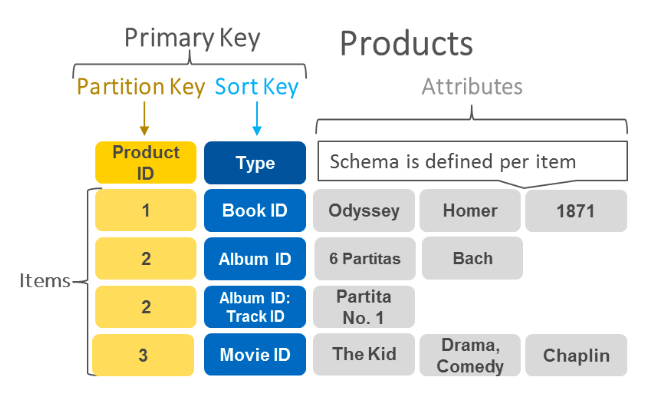
- Rows are items, and cells are attributes.
- Each table has a primary key:
- They can be either simple (a partition key) or composite (a partition key and a sort key)
- The partition key tells what partition will physically store the data.
- Partition keys and sort keys can contain only one attribute.
Consistency
- Eventual consistent reads:
- The response might not reflect the results of a recently completed write operation.
- If you repeat your read request after a short time, the response should return the latest data.
- Strongly consistent reads:
- DynamoDB returns a response with the most up-to-date data.
- For example, for a financial algorithm of life critical systems or a booking system.
- A strongly consistent read might not be available if there is a network delay or outage.
- Associated with an increased cost.
ElastiCache
- ElastiCache is a web service to deploy, operate, and scale in-memory cache in the cloud.
- Improves performance of web applications by allowing to retrieve information from fast, managed, in-memory caches, instead of relying entirely on slower disk-based databases.
- Supports two open-source in-memory caching engines: Memcached and Redis.
- For a simple cache to offload DB, use Memcached.
- For a cache with more advanced capabilities (Multi-AZ, backups), use Redis.
- Elasticache for Memcached does not offer a native encryption service, while Elasticache for Redis does.
- Although the name only suggests caching functionality, the Redis service in particular can offer a number of operations such as Pub/Sub, Sorted Sets and an In-Memory Data Store.
- Use Redis AUTH command to improve data security by requiring the user to enter a password before they are granted permission to execute Redis commands on a password-protected Redis server.
- Include
--auth-tokenwith the password when creating/modifying the replication group. - Authenticating Users with the Redis AUTH Command
- Include
- Amazon ElastiCache
- Amazon Elasticache Cheat Sheet
Redshift
- Data warehouses:
- Used for business intelligence (tools such as SAP NetWeaver)
- Used to pull in very large and complex datasets.
- Usually used by management to do queries on data (such as current performance)
- Amazon's data warehouse solution is called Redshift.
- Redshift is a fast and powerful, fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service.
- Can be configured as follows:
- Single node (160GB)
- Multi-node: Leader node that manages client connections and receives queries, and compute node that stores data and performs queries and computations. Up to 128 compute nodes are permitted.
- Employs multiple compression techniques.
- When loading data into Redshift, it automatically samples the data and select the most appropriate compression scheme.
- Massively Parallel Processing (MPP):
- Automatically distributes data and query load across all nodes.
- Redshift makes it easy to add nodes and enables you to maintain fast query performance.
- Doesn't require indexes or materialized views, and so uses less space.
- Backups:
- Enabled by default with a 1 day retention period.
- Maximum retention period is 35 days.
- Always attempts to maintain at least three copies of data (the original and replica on the compute nodes and a backup in S3)
- Can asynchronously replicate snapshots to S3 in another region for disaster recovery.
- Priced as follows:
- Compute node hours (1 unit per node per hour), but not charged for leader node hours.
- Data transfer (only within a VPC, not outside it)
- Backups
- Encryption:
- Encrypted in transit using SSL.
- Encrypted at rest using AES-256 encryption.
- By default Redshift takes care of key management.
- But you can manage your keys using HSM or AWS KMS.
- Availability:
- Currently available in one AZ.
- Can restore snapshots to new AZ in the event of an outage.
- Workload management (WLM):
- In Amazon Redshift, you use workload management (WLM) to define the number of query queues that are available, and how queries are routed to those queues for processing.
- WLM is part of parameter group configuration.
- A cluster uses the WLM configuration that is specified in its associated parameter group.
- Configuring Workload Management
- Amazon Redshift Enhanced VPC Routing:
- Amazon Redshift forces all COPY and UNLOAD traffic between your cluster and your data repositories through your Amazon VPC.
- You use these features to manage the flow of data between Redshift cluster and other resources.
- If disabled, Amazon Redshift routes traffic through the Internet.
- Amazon Redshift Enhanced VPC Routing
- Amazon Redshift Cheat Sheet



