Security, Identity, & Compliance
- AWS Security Best Practices
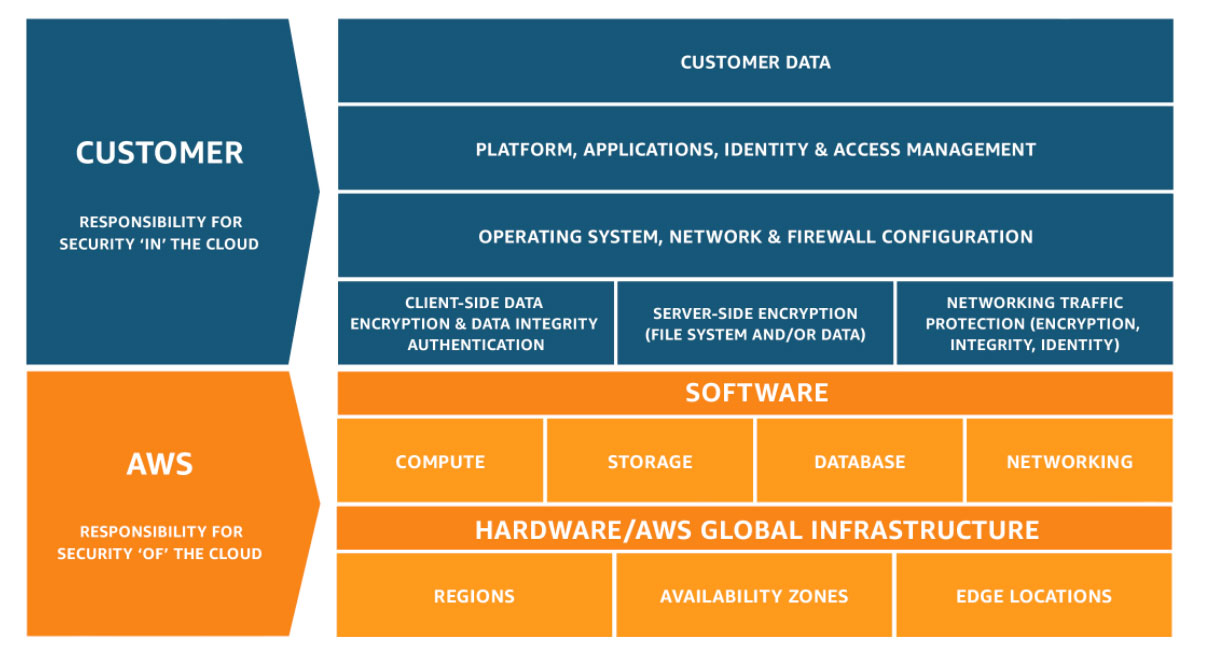
- Shared Security Responsibility Model
- Security “of” the cloud versus security “in” the cloud.
- Security and Compliance is a shared responsibility between AWS and the customer.
- Customers should carefully consider the services they choose as their responsibilities vary.
IAM
- IAM allows to manage users and their level of access to the AWS console.
- IAM is universal and is not region-specific at this time.
- Identity access management (IAM) offers the following features:
- Centralized control of the AWS account
- Shared access to the account
- Fine-grained access control to AWS resources
- Identity federations (Facebook, Linkedin, etc.)
- Multi-factor authentication
- Provides temporary access for users/devices and services when necessary.
- Allows to set up own password rotation policy.
- The "root account" is simply the account created with the AWS account.
- Owner:
- The Owner refers to the identity and email address used to create the AWS account.
- Comes into play especially when setting or locking down access to various objects.
- Users:
- End users such as employees of an organization.
- New users have no permissions by default.
- To access the AWS Management Console, new users use the account and password combination.
- To access the AWS programmatically, they use the access key & secret access key combination.
- Credentials can be viewed only once, thus save them in a secure location.
- Set up multi-factor authentication (MFA) to the root account (easy with Google Authenticator)
- Groups:
- Groups are collections of users.
- Each user inherits the permissions of the group.
- Policies:
- A policy is a JSON document that provides formal statement of one or more permissions.
- For example, allow user to access of all AWS services except the IAM service (power user)
- Configure users and policy documents only once, as these are applied globally.
- Roles:
- Give permissions to AWS services to use other AWS services.
- Tips:
- Enact a strong password policy: user passwords must be changed every 45 days, with each password containing a combination of capital letters, lower case letters, numbers, and special symbols.
- If you create an individual user for each staff member, there will be no way to keep their active directory credentials synched when they change their password. You should either create a federation proxy or identity provider and then use AWS security token service to create temporary tokens. You will then need to create the appropriate IAM role for which the users will assume when accessing AWS resources.
- AWS IAM Cheat Sheet
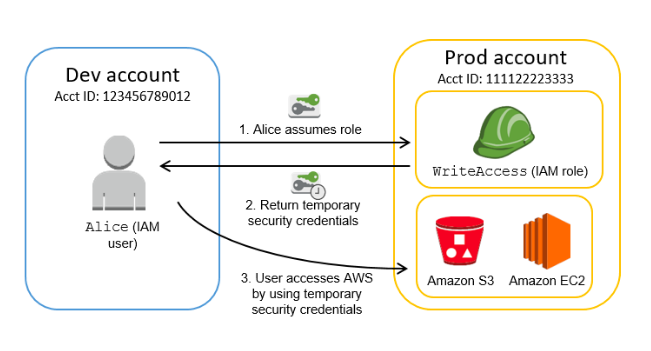
STS
- AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) is the service that you can use to create and provide trusted users with temporary security credentials that can control access to your AWS resources.
- Temporary Security Credentials
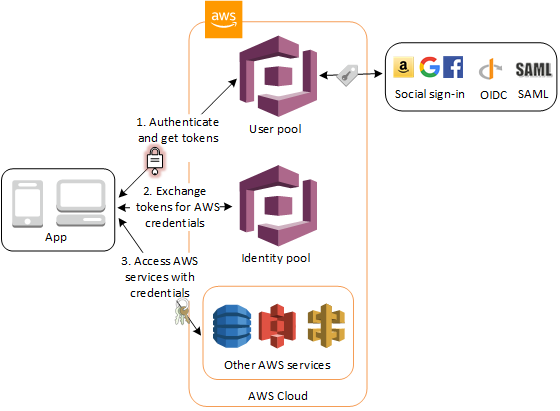
Cognito
- Web Identity Federation:
- Web Identity Federation lets you give your users access to AWS resources after they have successfully authenticated with a web-based identity provides such as Amazon, Facebook, or Google.
- It does not utilize Active Directory.
- Identity Providers and Federation
- You can use Amazon Cognito to deliver temporary, limited-privilege credentials to your application so that your users can access AWS resources.
- Following successful authentication, the user receives an authentication code from the Web ID provider, which they can trade for temporary AWS security credentials.
- Amazon Cognito provides WIF with the following features:
- Sign-up and sign-in to your apps.
- Enables access for guest users.
- Acts as an identity broker between application and Web ID providers.
- Providers temporary credentials that map to an IAM role allowing access to the required resources.
- No need for the application to embed or store AWS credentials.
- Gives seamless experience across all mobile devices.
- Tracks the association between user identity and the various devices they sign-in from.
- Uses Push Synchronization to push updates and to synchronize user data across devices.
- Uses SNS to send notifications whenever data stored in the cloud changes.
- Cognito User Pools:
- Take care of user registration, authentication and account recovery.
- User pools are user directories used to manage sign-up and sign-ins.
- Authentication generates a JSON Web Token (JWT)
- You can retrieve a unique Amazon Cognito ID for your end user immediately.
- Cognito Identity Pools:
- Take care of granting rights to AWS resources (authorization)
- Enable temporary AWS credentials to access AWS services like S3 or DynamoDB.
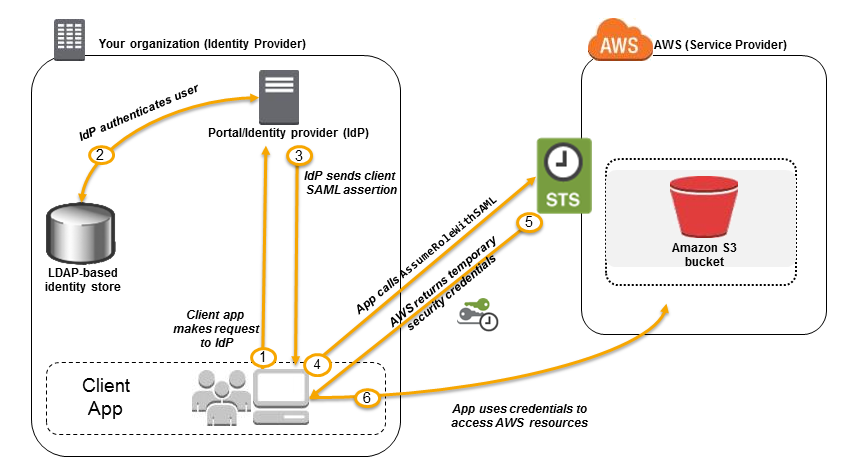
SAML
- In an enterprise identity federation, you can authenticate users in your organization's network, and then provide those users access to AWS without creating new AWS identities for them and requiring them to sign in with a separate user name and password.
- SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language 2.0) gives your federated users single sign-on (SSO) access to the AWS Management Console.
- An open standard that many identity providers (IdPs) use, for example, Microsoft Active Directory.
- This feature enables federated single sign-on (SSO), so users can log into the AWS Management Console or call the AWS APIs without you having to create an IAM user for everyone.
- With SAML-enabled single sign-on, the portal first verifies the user's identity in your organization, then generates a SAML authentication response. After the client posts the SAML assertion, AWS sends the sign-in URL as a redirect, and the client browser is redirected to the console.
- About SAML 2.0-based Federation
Directory Service
- AWS Directory Service provides multiple ways to use Amazon Cloud Directory and Microsoft Active Directory (AD) with other AWS services.
- Directories store information about users, groups, and devices.
- Administrators use them to manage access to information and resources.
- Using a corporate Active Directory, it is best to use AWS Directory Service AD Connector:
- It is a directory gateway with which you can redirect directory requests to your on-premises Microsoft Active Directory.
- AWS Directory Service Simple AD just provides a subset of the features offered by AWS Managed Microsoft AD, including the ability to manage user accounts and group memberships, create and apply group policies, securely connect to Amazon EC2 instances, and provide Kerberos-based single sign-on (SSO).
- How to Connect Your On-Premises Active Directory
- AWS Directory Service Cheat Sheets
- Introduction to AWS Directory Service
Data protection
KMS
- AWS Key Management Service (KMS) makes it easy for you to create and manage keys and control the use of encryption across a wide range of AWS services and in your applications.
- Create, import, disable and re-enable keys and define key management roles in IAM.
- AWS KMS is also integrated with AWS CloudTrail to provide encryption key usage logs to help meet your auditing, regulatory and compliance needs.
- You can configure your application to use the KMS API to encrypt all data before saving it to disk.
- AWS Key Management Service Concepts
- AWS KMS Cheat Sheet
Macie
- Amazon Macie is a security service that uses machine learning to automatically discover, classify, and protect sensitive data in AWS.
Service protection
WAF
- Web Application Firewall is a firewall that helps protect web applications from common web exploits.
- The following conditions are supported: Cross-site scripting, Geo, IP, Size, SQL injection, and String and regex match conditions.
Shield
- AWS Shield is a managed Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) protection service.
- Operates on layer 3 and 4 of the ISO network model.
- AWS Shield Advanced:
- Provides additional detection and mitigation against large and sophisticated DDoS attacks, near real-time visibility into attacks, and integration with AWS WAF, a web application firewall.
- Gives you 24x7 access to the AWS DDoS Response Team (DRT)
- AWS Best Practices for DDoS Resiliency

