Compute
EC2
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a web service that provides resizable compute capacity.
- Reduces the time required to obtain and boot new server instances (from days) to minutes.
- A huge side-effect of both of these: it’s way easier to innovate.
- Allows quickly scaling capacity, both up and down, as requirements change.
- Location:
- Individual instances are provisioned in a AZ.
- When planning a number of instances per AZ, always assume that the AZ you lose is the one with the most instances.
- Instances can be moved to AZ via AMIs and to regions via "Copy AMI".
- By default, AWS has a limit of 20 instances per region per account.
- You should submit the limit increase form for the limit to be... increased.
- Bootstrap scripts:
- Run when the EC2 instance first boots.
- Can be a powerful way of automating software installs and updates.
# Example: Bootstrap script for a simple Apache server
#!/bin/bash
yum update -y
yum install httpd -y
service httpd start
chkconfig httpd on
cd /var/www/html
echo "<html><h1>Hello, World!</h1></html>" > index.html
- Accessing instance metadata from within:
- Instance metadata and user data can be retrieved from within via a special URL.
- You can get the instance ID, public keys, public IP address and many other information from the instance metadata by running
curl http://169.256.169.254/latest/meta-data/ - Get user data by running
curl http://169.256.169.254/latest/user-data/ - For example, EC2 can access its public IP address and write it to a database.
- Note: the metadata under these addresses can be only read, but not managed.
- For spot instances, 120 seconds before the termination, AWS will create a flag in metadata.
- Roles:
- Roles are more secure and easier to manage than via
aws configureon EC2. - Roles can be assigned to EC2 instances after its created.
- Roles are universal (global) and take effect immediately.
- Roles are more secure and easier to manage than via
- Authentication:
- Verify that you are connecting with the appropriate user name for your AMI (e.g.
ec2-user) - Verify that your private key file has the correct format (e.g.
.pem,.ppk)
- Verify that you are connecting with the appropriate user name for your AMI (e.g.
- Metadata can be assigned using tags.
- Tagging is a key part of managing an environment.
- Instance Lifecycle:
- If the instance is stopped, AWS usually moves the instance to a new host computer.
- Your instance may stay on the same host computer if there are no problems.
- Termination protection is turned off by default.
- Docker containers:
- Only ECS, Elastic Beanstalk and Fargate allow containers to run natively.
- EC2 instances can run Docker containers, but Docker has to be installed separately.
- General EC2 logging guidance:
- Set up a Flow Log for the group of instances and forward them to CloudWatch/S3.
- Make use of an OS-level logging tools such as
iptablesand log events to CloudWatch/S3.
- Billing:
- Pay as you go, pay for what you use, and pay even less for reserved instances.
- Simply stop the instances will eliminate charges until the instances are restarted.
- Transferring data from an EC2 instance to Amazon S3, Amazon Glacier, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon SES, Amazon SQS, or Amazon SimpleDB in the same AWS Region has no cost at all.
- Bring Your Own IP Addresses (BYOIP)
- You can bring your public IPv4 address range from your on-premises network to your AWS account.
- The Route Origin Authorization (ROA) authorizes Amazon to advertise this address range.
- There are two underlying hypervisors for EC2:
- Xen and Nitro (newer)
- Amazon EC2 FAQs
- Amazon EC2 Cheat Sheet
Pricing
- On demand:
- Fixed rate by hour (or by second) with no up-front payment or commitment.
- For applications with short term, spiky, or unpredictable workloads that cannot be interrupted.
- For applications that are tested for the first time.
- Reserved Instances:
- Capacity reservation with significant discounts, one or three years contracts.
- For applications with steady state and predictable usage.
- For applications that require reserved capacity.
- Users can do up-front payments to reduce their total computing costs even further.
- Standard Reserved Instances: The higher the upfront payment and the longer the contract, the greater the discount (up to 75% off)
- Convertible Reserved Instances: Attributes can be changed dynamically as long as the new instances is of equal or greater value (up to 54% off)
- Scheduled Reserved Instances: Enable you to purchase capacity reservations that recur on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, with a specified start time and duration, for a one-year term. “I just need extra on Black Friday, but that’s it”
- Types of Reserved Instances (Offering Classes)
- Spot instances:
- Have a huge isolated workload? Snag a spot instance when the price is super cheap at 4AM on a Tuesday, run your stuff, then shut it all down.
- Whenever the price goes up, these instances will be terminated.
- If AWS terminates your instance in the first hour, there is no charge.
- If AWS terminates your instance after the first hour, you will be charged for the actual time that the instance was running (down to the second.
- For applications that have flexible start and end times.
- For applications that are only feasible at very low computing prices.
- For users with urgent computing needs for large amounts of additional capacity.
- You cannot stop a spot instance.
- If your spot instances get terminated too often, you should consider either increasing the bid price for the task nodes so that your nodes are not terminated or even converting the task nodes to on demand instances so as to ensure they are not prematurely terminated.
- New Spot Instance Termination Notice
- Dedicated hosts:
- Physical EC2 server dedicated for own use.
- Allows to use existing server-bound software licenses like VMWare and Oracle.
- For regulatory requirements that may not support multi-tenant virtualization.
- For licensing that does not support multi-tenant virtualization or cloud deployment (Oracle)
- Can be purchased on-demand.
- Can be purchased as a reservation for up to 70% off the on-demand price.
- The tenancy of an instance can only be change between variants of ‘dedicated' tenancy hosting: Dedicated & Host. It cannot be changed from or to default tenancy hosting.
Instance types

- Fight Dr. McPXZ in Australia
- FIGHT:
- F (Field programmable gate array): Genomic research, financial analysis, big data
- I (IOPS): NoSQL, data warehouses
- G (Graphics intense): Video encoding, 3D application streaming
- H (High disk throughput): MapReduce, HDFS
- T (Cheap general purpose, T2 Micro): Web servers, small databases
- DR:
- D (Dense storage): File servers, data warehouses, Hadoop
- R (RAM optimized): Memory intensive applications or databases
- MC:
- M (Main choice for general purpose applications): application servers
- C (Compute optimized): CPU intensive applications or databases
- PXZ:
- P (Graphics, GPUs): Machine learning, Bitcoin mining
- X (Extreme memory): SAP HANA, Apache Spark
- Z (Extreme memory and CPU): Electronic design automation, high per-core licensing costs
- AU:
- A (Arm-based workloads): Scale-out workloads such as web servers
- U (Bare metal): Bare metal capabilities
Storage
- Amazon EBS
- Amazon EFS
- Storage backed by Amazon EBS:
- The root device is an Amazon EBS volume created from an Amazon EBS snapshot.
- EBS backed instances can be stopped since they get a new host when starting again.
- Can be rebooted without data loss.
- Storage backed by instance store:
- The word ephemeral means "short-lived" or "temporary" in the English dictionary.
- An instance store provides temporary block-level storage and is located on disks that are physically attached to the host computer.
- The virtual devices for instance store volumes are named as
ephemeral[0-23] - The root device is an instance store backed volume created from a template stored on S3.
- The instance store is ideal for temporary storage.
- Cannot be stopped: If the underlying host fails, the data will be lost.
- If an instance reboots (intentionally or unintentionally), data in the instance store persists.
- No automatic backups will be performed.
- It is a non-billable storage.
- Instance Store Lifetime
Placement groups
- Clustered placement group:
- Grouping of instances within a single AZ.
- Keeps compute resources within one network hop of each other on high speed rack switches.
- For applications that require low latency, high network throughput, or both.
- AWS recommends homogeneous instances with this group.

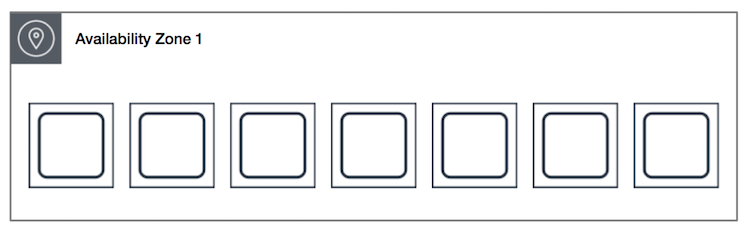
- Spread placement group:
- Grouping of instances that are each placed on distinct hardware.
- For applications that have critical instances that should be kept separate from each other.
- Can be located in different AZ's of one region.
- Allows to isolate the impact of hardware failure within application.
- Allows to have a maximum of 7 running instances per AZ.
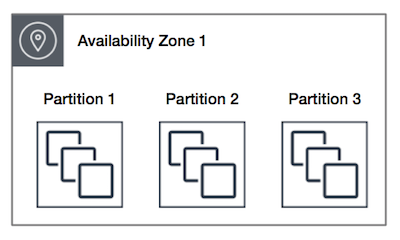
- Partitioned placement group:
- Same as spread placement group but allows multiple instances (e.g. Hadoop cluster)
- Divides each group into logical segments called partitions.
- Each partition has its own set of racks.
- Each rack has its own network and power sources.
- No two partitions within a placement group share the same racks.
- Allows to isolate the impact of hardware failure within application.
- Restrictions:
- Only certain instances can be launched within each group.
- The specified name must be unique within the AWS account.
- Placement groups can't be merged.
- An existing instance can't be moved into a placement group. For this, create an AMI from the existing instance, and then launch a new instance from the AMI into the placement group.
Elastic Beanstalk
- Quickly deploy and manage applications without worrying about infrastructure.
- Simply upload your application, and Elastic Beanstalk will automatically handle the capacity provisioning, load balancing, scaling, and health monitoring.
- Aimed at developers who don't know CloudFormation and want to get their stuff into AWS.
ECS
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a highly scalable, high-performance container orchestration service that supports Docker containers and allows you to easily run and scale containerized applications on AWS.
- Amazon ECS enables you to inject sensitive data into your containers by storing your sensitive data in either AWS Secrets Manager secrets or AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store parameters and then referencing them in your container definition.
- To inject sensitive data into your containers as environment variables, use the
secretscontainer definition parameter. - To reference sensitive information in the log configuration of a container, use the
secretOptionscontainer definition parameter. - Specifying Sensitive Data
- The Right Way to Store Secrets using Parameter Store
- To inject sensitive data into your containers as environment variables, use the
- Amazon ECS Cheat Sheet
Lambda
- AWS Lambda lets you run code without provisioning or managing servers = serverless.
- Takes care of provisioning and managing the servers that you use to run the code.
- Can be run in response to triggers, to HTTP requests using API Gateway, or API calls using AWS SDKs.
- API-Gateway Events, S3 Events and DynamoDB Events are all valid triggers for Lambda functions.
- Can trigger other Lambda functions.
- Can do things globally, for example, back up S3 buckets to other S3 buckets.
- For example, Amazon Alexa is directly speaking to Lambda.
- Lambda scales out automatically:
- Each time a Lambda function is triggered, an isolated instance of that function is invoked.
- Multiple triggers result in multiple concurrent invocations, one for each time it is triggered.
- There are limits, but these can be adjusted on request.
- Billing:
- Counts a request each time it starts executing in response to an event.
- Calculates duration from the time (in 100ms units) code begins executing until it returns or otherwise terminates.
- Depends on the amount of memory (in MB) you allocate to your function.
- Free tier includes 1M free requests per month and 400,000 GB-s of compute time per month.
- AWS X-Ray allows you to debug complex Lambda architectures.
- AWS X-Ray helps developers analyze and debug production, distributed applications, such as those built using a microservices & serverless architectures.
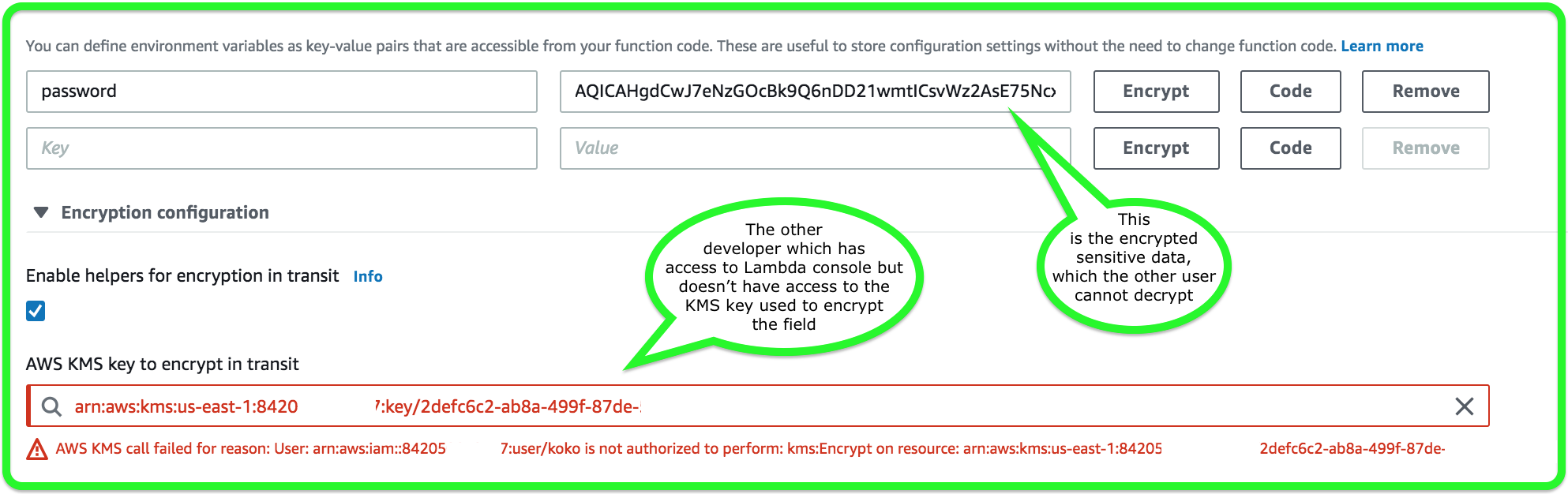
- Encryption of environment variables:
- AWS Lambda encrypts environment variables using the AWS Key Management Service.
- By default, the sensitive information is still visible when accessing the Lambda console.
- To prevent anyone from seeing these credentials in plain text, use encryption helpers.
- Creating your own key gives you more flexibility, including the ability to create, rotate, disable, and define access controls, and to audit the encryption keys used to protect your data.
- Environment Variable Encryption
- Deployment configuration types with AWS CodeDeploy:
- Allows you to shift traffic from one Lambda function to another.
- Canary: Traffic is shifted in two increments.
- Linear: Traffic is shifted in equal increments with an equal number of minutes in-between.
- All-at-once: All traffic is shifted at once.
- What Is CodeDeploy?
- Invoking AWS Lambda Functions
- AWS Lambda supports synchronous and asynchronous invocation of a Lambda function.
- AWS Lambda enables functions that can run up to 15 minutes.
- Lambda needs to have a role associated with it that provide credentials with rights to other services.
- Lambda like EC2 and ECS supports hyper-threading on one or more virtual CPUs.
- AWS Lambda Cheat Sheet
Athena
- Amazon Athena is an interactive query service to analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL.
- Athena is serverless, so there is no infrastructure to manage.
- Works with a number of data formats including JSON, Apache Parquet, and Apache ORC amongst others.
