Query Engines
Apache Hive

- Apache Hive is a data warehouse system built on top of Apache Hadoop that facilitates easy data summarization, ad-hoc queries, and the analysis of large datasets stored in various databases and file systems that integrate with Hadoop.
- Data warehouse refers to a system used for reporting and data analysis.
- Hive was initially developed at Facebook.
- Offers a simple way to apply structure to unstructured data to perform SQL-like queries.
- Takes unstructured data and applies a schema to it when the data is read.
- Data remains untouched.
- Hive maintains a "metastore" (HCatalog) that stores information such as data location and schema.
- Once a a Hive table is created, columns, rows, data types, etc., are stored in the metastore.
- Other tools such as Spark, Pig and Tableau can then access the data in the metastore.
- Hive enables data serialization/deserialization and increases flexibility in schema.
- Hive looks like traditional database code with SQL access but has to adhere to the rules of Hadoop framework.
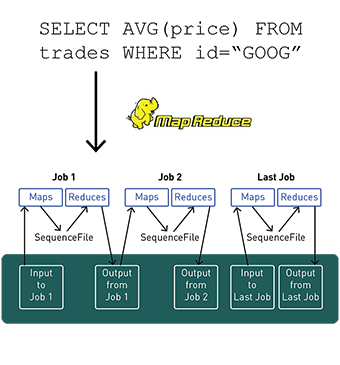
- Hive features an SQL-like programming interface called HiveQL:
- Pretty much MySQL with extensions (for example views)
- HiveQL automatically translates SQL-like queries into batch MapReduce jobs.
- In addition, HiveQL supported custom MapReduce scripts to plug into queries.
- It is possible to have full ACID properties in HiveQL.
- Only basic support for indexes.
- HiveQL does not provide support for OLTP and view materialization
- Hive has many user-defined functions (UDFs) that offer effective ways of solving problems.
- Hive can take ownership of the data with
LOAD DATAcommand or a managed table. - Partitioning is a huge optimization if queries are only on certain partitions (e.g. country)
- Hive can take ownership of the data with
- Faster execution of HiveQL or SQL on top of Hadoop:
- Spark SQL can be used with the Hive metastore.
- HiveQL can run on the Spark execution engine.
- Apache Drill provides the ability to leverage the metadata in the Hive metastore for querying.
- Hive can run on Tez, allowing queries to run significantly faster.
- Impala leverages HiveQL and metastore to bring interactive SQL to Hadoop.
- Provides ease of use and compatibility with existing business applications through JDBC/ODBC.
- Users are able to connect with Hive using a command-line tool and a JDBC driver.
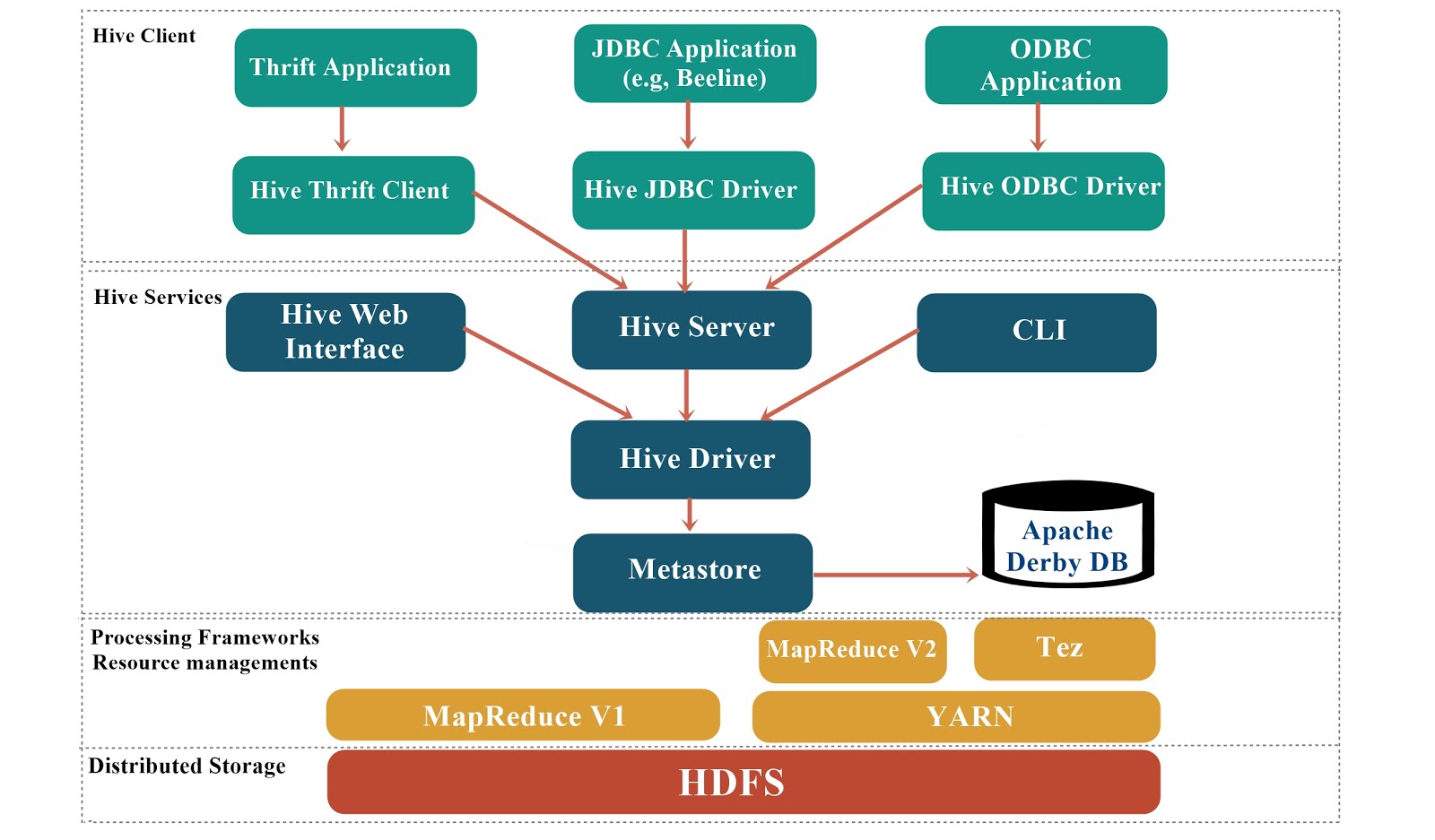
- Limitations:
- Hive is best suited for batch jobs, rather than working with web log data and append-only data.
- High latency: No fit for online transaction processing (OLTP) systems.
- Among highlights in release 3.0 in 2018 were support for ACID operations. Work also began on materialized views and automatic query rewriting capabilities familiar to traditional data warehouse users.
- How to Process Data with Apache Hive
-- Example: Find the most popular movie
CREATE VIEW IF NOT EXISTS topMovieIDs AS
SELECT movieID, count(movieID) as ratingCount
FROM ratings
GROUP BY movieID
ORDER BY ratingCount DESC;
SELECT n.title, ratingCount
FROM topMovieIDs t JOIN names n ON t.movieID = n.movieID;
Compared to Apache Impala
- Apache Impala is a massively parallel SQL engine on Hadoop.
- It's Cloudera's alternative to Hive.
- Consider using Impala instead of Hive if you're using Cloudera.
- It's often faster than Hive, but Hive offers more versatility and connectivity.
- Impala's always running thus avoiding start-up costs.
Apache Pig

- Pig is an abstraction built on top of MapReduce for rapid iteration and easy development.
- Can be run in local mode for small datasets.
- Can be run on top of TEZ (up to 10x faster)
- Pig consists of two components:
- Pig Latin, which is a language.
- A runtime environment, for running Pig Latin programs.
- Data transformations are explicitly encoded as data flow sequences, making them easy to write, understand, and maintain.
- Both, logical and physical plans are created to execute the Pig script.
- Pig is highly-extensible with user-defined functions (UDFs)
-- Example: Find old 5-star movies
-- Load relations
ratings = LOAD '/user/maria_dev/ml-100k/u.data' AS (userID:int, movieID:int, rating:int, ratingTime:int);
metadata = LOAD '/user/maria_dev/ml-100k/u.item' USING PigStorage('|') AS (movieID:int, movieTitle:chararray, releaseDate:chararray, videoRelease:chararray, imdbLink:chararray);
-- Get the average rating of each movie, filter, and order by the release date
nameLookup = FOREACH metadata GENERATE movieID, movieTitle, ToUnixTime(ToDate(releaseDate, 'dd-MMM-yyyy')) AS releaseTime;
ratingsByMovie = GROUP ratings BY movieID;
avgRatings = FOREACH ratingsByMovie GENERATE group AS movieID, AVG(ratings.rating) AS avgRating;
fiveStarMovies = FILTER avgRatings BY avgRating > 4.0;
fiveStarsWithData = JOIN fiveStarMovies BY movieID, nameLookup BY movieID;
oldestFiveStarMovies = ORDER fiveStarsWithData BY nameLookup::releaseTime;
DUMP oldestFiveStarMovies;
Compared to Hive
- Main focus of Pig is on bringing data into Apache Hadoop and getting it into the form for querying.
- Both Pig and Hive are feature complete.
- Hive is used more by researchers and programmers.
Distributed query engines
Apache Drill

- Apache Drill is a schema-free SQL Query Engine for Hadoop, NoSQL and Cloud Storage.
- Drill is the open source version of Google's Dremel.
- Extremely user and developer friendly.
- Designed to scale to several thousands of nodes and query petabytes of data interactively.
- Not tied to Hadoop and can run in any distributed cluster environment.
- Allows analysis of multi-structured and nested data in non-relational data stores.
- Supports a variety of NoSQL databases and file systems, including HBase, MongoDB, MapR-DB, HDFS, MapR-FS, Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage, Swift, NAS and local files.
- One can join a user profile collection in MongoDB with a directory of event logs in Hadoop.
- A new datastore can be added by developing a storage plugin.
- Integrates desperate data sources without data loading, schema creation, and transformations.
- Leverages advanced query compilation and re-compilation techniques to maximize performance.
- Internally data is represented as JSON to enable queries on complex/nested data.
- Schema-free JSON document model similar to MongoDB and Elasticsearch.
- Drill operators are designed to reconfigure themselves when schemas change.
- Does not have a centralized metadata requirement.
- One can use SQL DDL statements to create metadata within Drill.
- Features an in-memory shredded columnar representation for complex data.
- Supports ANSI SQL, ODBC/JDBC, RESTful APIs.
- Also supports dynamic UDFs.
- Architecture Introduction
-- Example: Joining tables from Hive and MongoDB
SELECT u.occupation, COUNT(*)
FROM hive.movielens.ratings r JOIN mongo.movielens.users u ON r.user_id = u.user_id
GROUP BY u.occupation;
Apache Phoenix

- Apache Phoenix is an open source, massively parallel, relational database engine supporting OLTP for Hadoop using Apache HBase as its backing store.
- Originally developed by Salesforce, then open-sourced.
- Offers flexibility of late-bound, schema-on-read capabilities from the NoSQL world.
- Supports SQL and JDBC APIs with full ACID transaction capabilities.
- Compiles SQL queries and other statements into native HBase APIs.
- Supports secondary indexes and UDFs.
- Integrates with MapReduce, Spark, Hive, Pig, and Flume.
- Why Phoenix and not HBase's native APIs?
- Apps and analysts may find SQL easier to work with.
- Can do the work of optimizing more complex queries.
-- Example: Populating HBase with Phoenix
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS us_population(
state CHAR(2) NOT NULL,
city VARCHAR NOT NULL,
population BIGINT,
CONSTRAINT my_pk PRIMARY KEY(state, city)
);
UPSERT INTO us_population VALUES ('NY', 'New York', 8143197);
UPSERT INTO us_population VALUES ('CA', 'Los Angeles', 3844829);
SELECT * FROM us_population WHERE state = 'CA';
Presto

- Presto is a distributed SQL query engine optimized for ad-hoc analysis at interactive speed.
- Allows users to query a variety of heterogeneous data sources:
- Optimized for both on-premise and cloud environments.
- Can natively query data in Hadoop, S3, Cassandra, MySQL, and many others.
- A single Presto query can combine data from multiple sources.
- For example, join historic log data in S3 with real-time customer data in MySQL.
- Was originally designed and developed at Facebook for their data analysts to run interactive queries.
- Presto was invented to fill the gap of Hive to run fast queries on petabyte DWH.
- PrestoDB is maintained by Facebook, while PrestoSQL is maintained by the Software Foundation.
- Facebook, Dropbox, and more use Presto for their huge bid data complex analytics.
Facebook uses Presto for interactive queries against several internal data stores, including their 300PB data warehouse. Over 1,000 Facebook employees use Presto daily to run more than 30,000 queries that in total scan over a petabyte each per day.
- Supports standard ANSI SQL, including complex queries, aggregations, joins, and window functions.
- Similar to a classic database management system using cluster computing (MPP).
- Optimized for OLAP - data warehousing and analytic. Was not designed for OLTP.
- Used for for critical business operations.
- Built with Java - for faster development.
- Exposes JDBC/ODBC, command-line, and industry BI interfaces.
- Presto provides a (sexy) web interface for monitoring and managing queries.
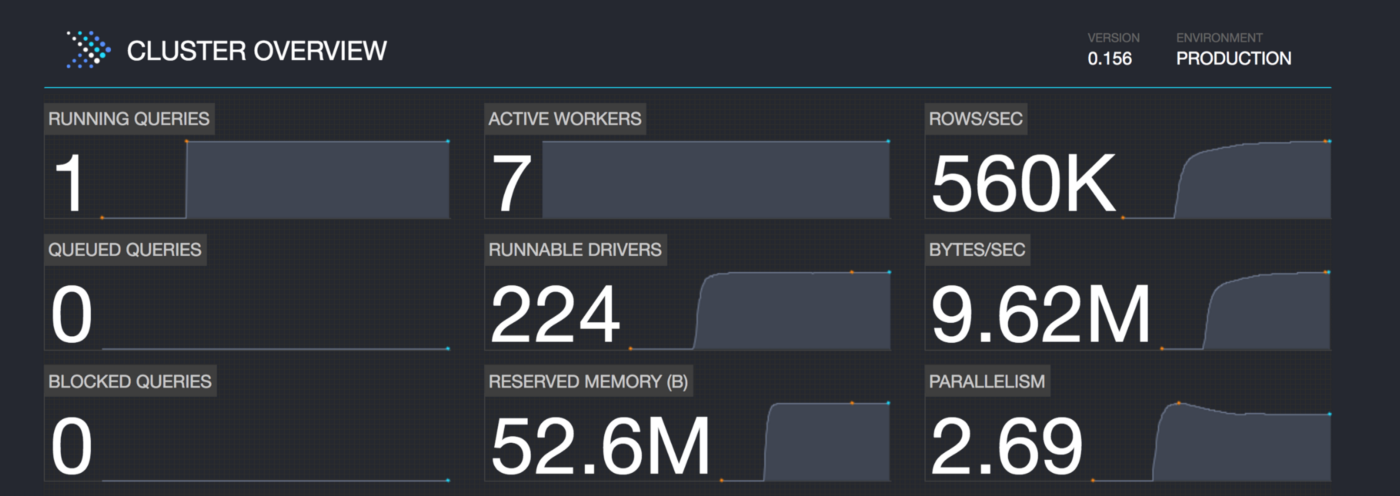
- As compared to Hive:
- Presto is an alternative to tools that query HDFS using pipelines of MapReduce jobs.
- Uses a more custom engine designed to support SQL semantics.
- Does not write intermediate results to disk.
- As compared to Apache Drill:
- Comes up with more support and technologies (e.g. Cassandra)
- Requires a schema to query data.
- Requires a more complex configuration.
- As compared to Apache Spark:
- Spark and Spark SQL have a greater and more mature ecosystem, more features, and used by many more organizations with more diverse requirements.
- What is the difference between Spark and Presto?
- 1.2. Presto Concepts
-- Example: Joining tables from Hive and Cassandra
SELECT u.occupation, COUNT(*)
FROM hive.movielens.ratings r JOIN cassandra.movielens.users u ON r.user_id = u.user_id
GROUP BY u.occupation;